top of page
Ara


Triple layer sign, Double layer sign, SIRE, Ped - 2
Double Layer Sign Double layer sign: Burada yer alan OCT kesiti incelendiğinde tam fovea altında ve genişce bir alanda retina pigment...


Triple layer sign, Double layer sign, SIRE, Ped - 1
Triple layer sign in ARMD


Choroidal neovascularization in Angioid Streaks
Choroidal neovascularization in angioid streaks


Florid Diabetic Retinopathy
Extensive ischemia of the retina in diabetic retinopathy


Optociliary shunt vessels
Optociliary shunt vessels are normal congenital vessels supporting the circulation between retina and choroid.


Capillary nonperfusion / capillary drop-out
Prominent ischemia of the retina in diabetic retinopathy


Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
A genetic choroidal disease causing age related macular degeneration

Combined choroidal neovascularization
Combined type 1 and type 2 choroidal neovascularisation in armd


Tuberculosis Chorioretinitis
Choroidal neovascular membrane secondary to choroidal tuberculosis granuloma


BALAD
Bacillary layer detachment, extensive changes in structure of the retina

Type 2 Neovascularisation
Type 2 neovascularisation in armd
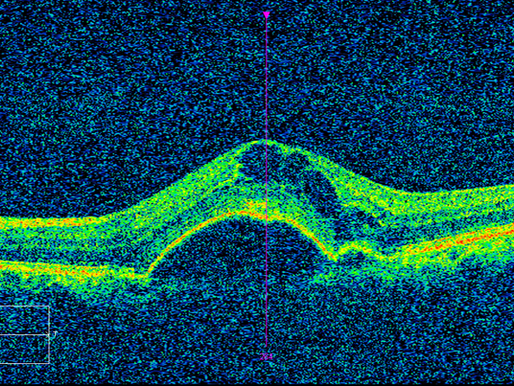
Retinal Angiomatous Proliferation (RAP)
neovascularisation in the retina, armd


Peripapillary Choroidal Neovascularisation
Choroidal neovascularisation originating from the peripapillary region


Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascular Membrane
Armd with choroidal neovascularisation underneath the fovea.


Juxtafoveal Chorodial Neovascular Membrane
Choroidal neovascularisation adjacent to foveal region


Extramacular Choroidal Neovascular Membrane
Armd, choroidal neovascularisation far away from the foveal center


Type 1 Neovascularisation
Most frequently encountered choroidal neovascularisation type in armd


Idiopathic Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
A rare subtype of armd, there are more cases diagnosed in recent years.

Vascularized Pigment Epithelial Detachment
May be accepted as precursor findings of choroidal neovascularisation

Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tears
A rare but devastating complication of both the disease itself and treatment in armd.
bottom of page
